Various forms of aluminum are components of some vaccine products. What is an adjuvant?
From the CDC: “An adjuvant is an ingredient of a vaccine that helps create a stronger immune response in the patient’s body. In other words, adjuvants help vaccines work better. Some vaccines made from weakened or dead germs contain naturally occurring adjuvants and help the body produce a strong protective immune response. However, most vaccines developed today include just small components of germs, such as their proteins, rather than the entire virus or bacteria. These vaccines often must be made with adjuvants to ensure the body produces an immune response strong enough to protect the patient from the germ he or she is being vaccinated against.”
Yet the safety of injecting aluminum has been questioned for decades. In 2022, the CDC finally performed a study to look at one condition, asthma, that has long been reported as being possibly linked to aluminum adjuvant exposure, but never studied.
From the authors of a 2022 CDC that found an association between aluminum and persistent asthma:
“CONCLUSION: In a large observational study, a positive association was found between vaccine-related aluminum exposure and persistent asthma. While recognizing the small effect sizes identified and the potential for residual confounding, addi- tional investigation of this hypothesis appears warranted.”
“It is theoretically possible that exposure to aluminum through vaccination could produce an immune profile biased toward Th2 and away from T helper 1 cell (Th1) immune responses. This hypothesis is a speculative one, because it is based on limited data from animal studies and has not to our knowledge been investigated in humans.” [bold added]
Have these agencies studied other biological effects of injected aluminum on humans? The authors of the study state in the discussion section of their paper:
“It appears biologically plausible that the intended effect of aluminum adjuvants is not the only biologic effect (ie, enhanced immunogenicity against vaccine- preventable diseases) of parenteral administration of aluminum adjuvants in early childhood.”
Federal oversight agencies have failed in their mandated duty to ensure product safety and they have completely ignored the published, peer-reviewed work of independent scientists that reveal great cause for concern.
LINK to Dr. Shaw’s Study. The video was produced for the brilliant film that is more important now than ever to watch: The Greater Good Movie. Notice the similarity with what is happening now with COVID shots? The silencing of risks and silencing those harmed is nothing new. This has been Public Health’s policy and the Drug Industry’s profit strategy for far too long.
Is the amount of aluminum allowed in a vaccine administered to a newborn based on safety studies? Is the dose based on the infant’s weight? On the amount of aluminum a newborn’s kidneys can safely eliminate? On the fragile state of the child’s developing immune and neurological systems? On the current science of aluminum particle neurotoxicity?
No.
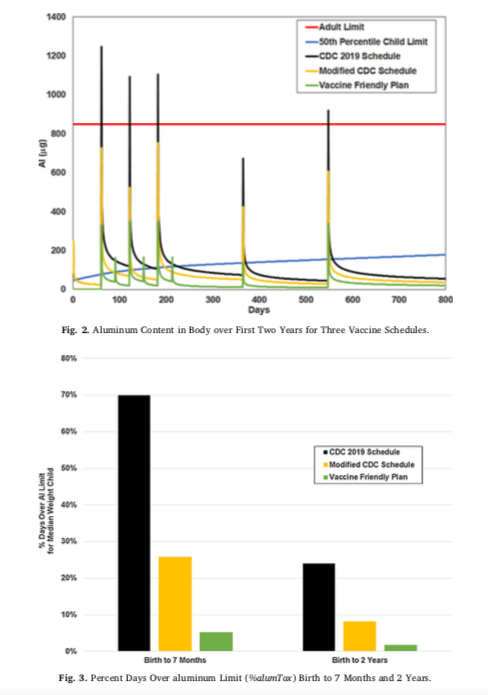
This 2018 paper reveals how the FDA determined the allowable amount of aluminum in a single vaccine–the same amount for a 7lb newborn as a 160lb adult–and reveals that it is absolutely critical for everyone who administers vaccines to children to cease following the CDC’s pediatric schedule and begin considering what is best for their young patients.
For an explanation of how the aluminum adjuvants in vaccines can lead to autism, see this article:
From VaccinePapers.org:
“The Dwoskins had attended the Institute of Medicine (IOM) and FDA meetings on vaccines, where aluminum was briefly discussed. Both the IOM and FDA acknowledged that aluminum adjuvant toxicity had not been studied. Inferences had been made, based on single-vaccine studies, but experiments to measure the toxicity of aluminum adjuvant had never been done (except by Shaw). In particular, nobody had ever tested the effect of the total amount of aluminum adjuvant received from the vaccine schedule recommended by the CDC.”
For the results of aluminum-adjuvant injection experiments that replicated the CDC pediatric schedule, visit VaccinePapers.org. Key findings: Administration of aluminium to neonatal mice in vaccine-relevant amounts is associated with adverse long term neurological outcomes.
Aluminum exposure during pregnancy
Pregnant women are being told that they are being given vaccines to protect the baby in language that implies, if not outright states, that appropriate safety studies have been done. They have not. Pregnant women in the general population are in essence being used in ongoing clinical trials without their fully informed consent.
Over the years, data has been gathered in a haphazard fashion using voluntary registries set up by pharmaceutical companies and in adverse event reports to VAERS, both of which suffer from extreme under-reporting. VSD (Vaccine Safety Datalink) studies on the safety of vaccination during pregnancy mostly include only pregnancies with live-birth outcomes, and very few studies look at the long-term health effects on children. One such rare study on vaccination with the influenza vaccine during pregnancy (Zerbo et al) found a significant association with autism. Even the most elaborate and inappropriate application of adjustments and corrections could not make the association go away in the first trimester, so the authors simply dismissed the result as due to chance. This is not science. http://jamanetwork.com/journals/jamapediatrics/article-abstract/2617988
The impact of maternal immune activation during pregnancy, and the impact of exposure to various vaccine components, such as the placenta-crossing 250 mcg of aluminum in the Tdap, on long-term neurological development are not known, but there’s enough science indicating that extreme caution is warranted. The current push to vaccinate during every single pregnancy, as well as during every outbreak, comes without any understanding of the health effect of such frequent administration of three disease antigens (tetanus, diphtheria, pertussis) and other vaccine components. This is a small sampling of studies on one component, aluminum:
-
- Multifaceted effects of aluminium in neurodegenerative diseases: A review. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/27479193
- Aluminum exposure and toxicity in neonates: a practical guide to halt aluminum overload in the prenatal and perinatal periods https://doi.org/10.1007/s12519-014-0477-x
- Mechanisms of aluminum adjuvant toxicity and autoimmunity in pediatric populations. https://doi.org/10.1177/0961203311430221
- Prenatal exposure to neurotoxicants and neurodevelopment in Mexican neonates. http://www.nature.com/jes/journal/v22/n4/full/jes201248a.html
- Non-linear dose-response of aluminium hydroxide adjuvant particles: Selective low dose neurotoxicity. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/27908630
- Association between prenatal exposure to metals and neonatal morbidity. http://www.tandfonline.com/doi/abs/10.1080/15287394.2014.932313
- There are many studies showing the neurotoxic effects of aluminum from environmental sources such as food. Only .3% of ingested aluminum is absorbed while 100% of injected aluminum is absorbed. These studies indicate the critical need for aluminum adjuvant safety research.
- Aluminum Exposure at Human Dietary Levels for 60 Days Reaches a Threshold Sufficient to Promote Memory Impairment in Rats. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/27473855
- In ovo toxico-teratological effects of aluminum on embryonic chick heart and vascularization https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/27535157
- A histological study of toxic effects of aluminium sulfate on rat hippocampus. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/25314162
- The consequences of aluminium intake on reproductive function in male rats: a three-generation study. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/27513431
Aluminum in Current FDA Licensed Vaccines
 Loading...
Loading...
Sourced from https://www.vaccinesafety.edu/excipients-in-vaccines-per-0-5-ml-dose/
Aluminum Toxicity Studies
2002 “Neurological adverse events associated with vaccination.”
2002 “The potential role of aluminium in Alzheimer’s disease.”
2004 “Neurotoxic effects of aluminium among foundry workers and Alzheimer’s disease.)
2007 “Aluminum adjuvant linked to Gulf War illness induces motor neuron death in mice.”
2007 “Mechanisms of aluminum-induced neurodegeneration in animals: Implications for Alzheimer’s disease.”
2007 “Inflammation, neurodegenerative diseases, and environmental exposures.”
2009 “Aluminum hydroxide injections lead to motor deficits and motor neuron degeneration.”
2011 “Aluminum toxicity and astrocyte dysfunction: a metabolic link to neurological disorders.”
2011 “Aluminum vaccine adjuvants: are they safe?”
“Aluminum is an experimentally demonstrated neurotoxin and the most commonly used vaccine adjuvant. Despite almost 90 years of widespread use of aluminum adjuvants, medical science’s understanding about their mechanisms of action is still remarkably poor. There is also a concerning scarcity of data on toxicology and pharmacokinetics of these compounds. In spite of this, the notion that aluminum in vaccines is safe appears to be widely accepted. Experimental research, however, clearly shows that aluminum adjuvants have a potential to induce serious immunological disorders in humans. In particular, aluminum in adjuvant form carries a risk for autoimmunity, long-term brain inflammation and associated neurological complications and may thus have profound and widespread adverse health consequences. In our opinion, the possibility that vaccine benefits may have been overrated and the risk of potential adverse effects underestimated, has not been rigorously evaluated in the medical and scientific community.”
2011 “Metal ions affecting the neurological system.”
2013 “Autoimmune/autoinflammatory syndrome induced by adjuvants (ASIA syndrome) in commercial sheep.”
2014 “Aluminum-induced entropy in biological systems: implications for neurological disease.”
2014 “Are there negative CNS impacts of aluminum adjuvants used in vaccines and immunotherapy?”
“Being involved in the production of reactive oxygen species, aluminium may impair mitochondrial bioenergetics and may lead to the generation of oxidative stress. In this review, we have discussed the oxidative stress and mitochondrial dysfunctions occurring in Al neurotoxicity. In addition, the ameliorative measures undertaken in aluminium induced oxidative stress and mitochondrial dysfunctions have also been highlighted.”
2015 “Trace elements in scalp hair samples from patients with relapsing-remitting multiple sclerosis.”
2015: “Biopersistence and brain translocation of aluminum adjuvants of vaccines”
“We previously showed that poorly biodegradable aluminum-coated particles injected into muscle are promptly phagocytosed in muscle and the draining lymph nodes, and can disseminate within phagocytic cells throughout the body and slowly accumulate in brain. This strongly suggests that long-term adjuvant biopersistence within phagocytic cells is a prerequisite for slow brain translocation and delayed neurotoxicity.”
“We demonstrate that not all aluminium adjuvants are equal neither in terms of their physical properties nor their biological reactivity and potential toxicities both at the injection site and beyond. High loading of aluminium oxyhydroxide in the cytoplasm of THP-1 cells without immediate cytotoxicity might predispose this form of aluminium adjuvant to its subsequent transport throughout the body including access to the brain.”.
“Vaccine adjuvants and vaccines may induce autoimmune and inflammatory manifestations in susceptible individuals. To date most human vaccine trials utilize aluminum (Al) adjuvants as placebos despite much evidence showing that Al in vaccine-relevant exposures can be toxic to humans and animals. We sought to evaluate the effects of Al adjuvant and the HPV vaccine Gardasil versus the true placebo on behavioral and inflammatory parameters in female mice.”
“Although generally well tolerated on the short term, it has been suspected to occasionally cause delayed neurologic problems in susceptible individuals. In particular, the long-term persistence of aluminic granuloma also termed macrophagic myofasciitis is associated with chronic arthromyalgias and fatigue and cognitive dysfunction. Safety concerns largely depend on the long biopersistence time inherent to this adjuvant, which may be related to its quick withdrawal from the interstitial fluid by avid cellular uptake; and the capacity of adjuvant particles to migrate and slowly accumulate in lymphoid organs and the brain, a phenomenon documented in animal models and resulting from MCP1/CCL2-dependant translocation of adjuvant-loaded monocyte-lineage cells (Trojan horse phenomenon). These novel insights strongly suggest that serious re-evaluation of long-term aluminum adjuvant phamacokinetics and safety should be carried out.”
2017 Effects of Aluminium on Rat Brain Mitochondria Bioenergetics: an In vitro and In vivo Study
“The observed effects also included both an alteration in mitochondrial transmembrane potential and a decrease in oxidative phosphorylation capacity when relatively high concentrations of aluminium were added to the isolated mitochondria. These findings contribute to explain both the ability of aluminium to generate oxidative stress and its suggested potential to act as an etiological factor by promoting the progression of neurodegenerative disorders such as Parkinson’s disease.”
“Evidence of the neurotoxicity of aluminium cations (Al3+) includes: an association between chronic aluminium exposure and the development of AD; the involvement of aluminium adjuvants in the development of ASIA; and epidemiological evidence pointing to an association between the use of aluminium adjuvants and ASD.”
“Aluminium has no known beneficial physiological action in the human body and some genetic polymorphisms predispose to a greater susceptibility to its adverse effects. Therefore, a strong case can be made for avoiding unnecessary exposure to environmental sources of aluminium salts, especially on the part of children, pregnant mothers and women of child-bearing age who may become pregnant. Such avoidance need not lead to hardship or inconvenience; aluminium cookware may be replaced by safer alternatives, while aluminium-containing antiperspirants, potentially implicated in the rise of cases of breast cancer particularly affecting the upper outer quadrant of the mammary gland, may be replaced by non-aluminium versions. The use of aluminium salts in medical products is a more contentious issue. While antacids are available which do not contain aluminium salts, the avoidance of immunisations which do not contain aluminium salts as adjuvants has wider political and financial implications. It would seem prudent to try to find an alternative to aluminium adjuvants as soon as possible and phase out their use.”
“Moreover, aluminium exposure is associated with the production of pro-inflammatory cytokines and chemokines and with the development of chronic oxidative stress, mitochondrial dysfunction and glial activation or dysfunction; these changes in turn are associated with ASD.”
2017 Aluminium in brain tissue in autism.
“The pre-eminence of intracellular aluminium associated with non-neuronal cells was a standout observation in autism brain tissue and may offer clues as to both the origin of the brain aluminium as well as a putative role in autism spectrum disorder.”
2018 Critical analysis of reference studies on the toxicokinetics of aluminum-based adjuvants
“We reviewed the three toxicokinetic reference studies commonly used to suggest that aluminum (Al)-based adjuvants are innocuous. A single experimental study was carried out using isotopic 26Al (Flarend et al., Vaccine, 1997). This study used aluminum salts resembling those used in vaccines but ignored adjuvant uptake by cells that was not fully documented at the time. It was conducted over a short period of time (28 days) and used only two rabbits per adjuvant. At the endpoint, Al elimination in the urine accounted for 6% for Al hydroxide and 22% for Al phosphate, both results being incompatible with rapid elimination of vaccine-derived Al in urine. Two theoretical studies have evaluated the potential risk of vaccine Al in infants, by reference to an oral “minimal risk level” (MRL) extrapolated from animal studies. Keith et al. (Vaccine, 2002) used a high MRL (2 mg/kg/d), an erroneous model of 100% immediate absorption of vaccine Al, and did not consider renal and blood-brain barrier immaturity. Mitkus et al. (Vaccine, 2011) only considered solubilized Al, with erroneous calculations of absorption duration. Systemic Al particle diffusion and neuro-inflammatory potential were omitted. The MRL they used was both inappropriate (oral Al vs. injected adjuvant) and still too high (1 mg/kg/d) regarding recent animal studies. Both paucity and serious weaknesses of reference studies strongly suggest that novel experimental studies of Al adjuvants toxicokinetics should be performed on the long-term, including both neonatal and adult exposures, to ensure their safety and restore population confidence in Al-containing vaccines.”
2018 Reconsideration of the immunotherapeutic pediatric safe dose levels of aluminum
“Our calculations show that the levels of aluminum suggested by the currently used limits place infants at risk of acute, repeated, and possibly chronic exposures of toxic levels of aluminum in modern vaccine schedules. Individual adult exposures are on par with Provisional Tolerable Weekly Intake “limits”, but some individuals may be aluminum intolerant due to genetics or previous exposures. Vaccination in neonates and low birth-weight infants must be re-assessed; other implications for the use of aluminum-containing vaccines, and additional limitations in our understanding of neurotoxicity and safety levels of aluminum in biologics are discussed.”
“Contact allergy to aluminium was considered to be extremely rare1–3 until the 1990s, when an unexpectedly high number of cases (n = 377) was reported following vaccination with an aluminium-adsorbed acellular pertussis vaccine in clinical trials in the greater Gothenburg area in Sweden.4, 5 All vaccines against diphtheria, tetanus, and pertussis (DTP), hepatitis A and B, human papilloma virus and tick-borne encephalitis, as well as some conjugated vaccines against pneumococcal and meningococcal infections, are adsorbed to aluminium salts (mostly hydroxide and phosphate) as adjuvants. Most allergen extracts used for allergen-specific immunotherapy (“hyposensitization”) also contain aluminium adjuvants. Another side-effect of aluminium-adsorbed vaccines and allergen extracts that is associated with aluminium allergy is the formation of long-lasting, intensely itching subcutaneous nodules (granulomas) at the injection site.”
2020 An aluminium adjuvant in a vaccine is an acute exposure to aluminium
2022 Metabolic and Cellular Compartments of Acetyl-CoA in the Healthy and Diseased Brain
“However, SN56 cholinergic neurons with a high expression of cholinergic phenotype appeared to be more susceptible than nondifferentiated ones or glial cells to several neurotoxic signals that inhibited the PDHC, resulting in the suppression of acetyl-CoA synthesis in mitochondria. Such alterations took place in cholinergic neurons or brain nerve terminals upon exposure to several common neurotoxic signals, such as Aβ, Zn, NO-excess, Ca overload, thiamine deficiency, aluminium exposure and hypoxia.” (bold added).
“Similarly, aluminium NPs were studied for their ability to deliver the antigenic components of MERS-CoV and SAR-CoV to the host cells [13]. However, the cellular toxicity of these nanocarriers and/or the need for an adjuvant may be considered as significant limitations of such nano-based vaccines.”
“Aluminum (Al) salts are commonly used as adjuvants in human and veterinary vaccines for almost a century. Despite this long history of use and the very large number of exposed individuals, data in the literature concerning the fate of these molecules after injection and their potential effects on the nervous system is limited. In the context of (i) an increase of exposure to Al salts through vaccination; (ii) the absence of safety values determined by health regulators; (iii) the lack of robustness of the studies used as references to officially claim Al adjuvant innocuity; (iv) the publication of several animal studies investigating Al salts clearance/biopersistence and neurotoxicity; we have examined in this review all published studies performed on animals and assessing Al adjuvants kinetics, biodistribution, and neuromodulation since the first work of A. Glenny in the 1920s. The diversity of methodological approaches, results, and potential weaknesses of the 31 collected studies are exposed. A large range of protocols has been used, including a variety of exposure schedule and analyses methods, making comparisons between studies uneasy. Nevertheless, published data highlight that when biopersistence, translocation, or neuromodulation were assessed, they were documented whatever the different in vivo models and methods used. Moreover, the studies pointed out the crucial importance of the different Al adjuvant physicochemical properties and host genetic background on their kinetics, biodistribution, and neuromodulatory effects. Regarding the state of the art on this key public health topic, further studies are clearly needed to determine the exact safety level of Al salts.”
“CONCLUSION: In a large observational study, a positive association was found between vaccine-related aluminum exposure and persistent asthma. While recognizing the small effect sizes identified and the potential for residual confounding, additional investigation of this hypothesis appears warranted.”